I. Modification Technology of PTFE Step Rings
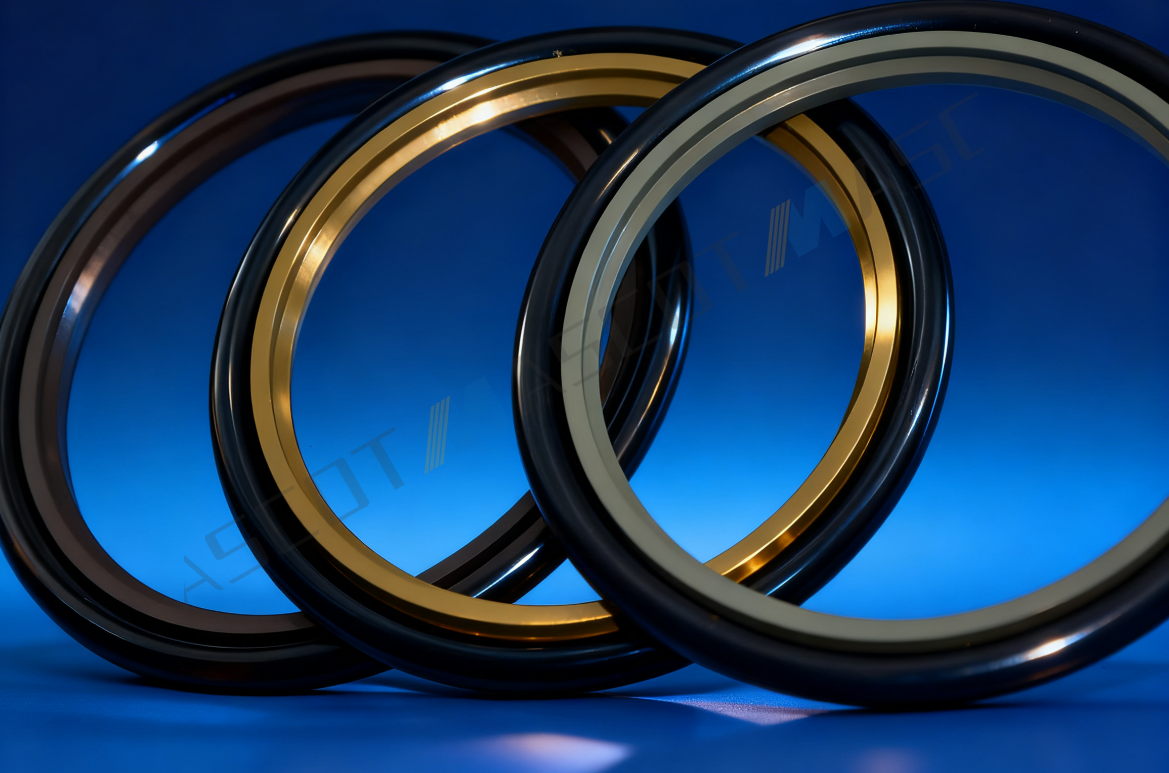
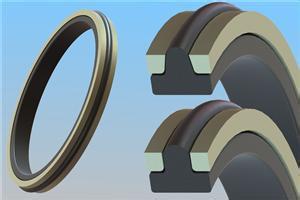

The PTFE step rings in Steck seals achieve significant performance enhancement through bronze powder filling. After filling, the friction coefficient of PTFE decreases from 0.04–0.2 (for pure PTFE) to 0.02–0.04, and its wear resistance increases by approximately 300%. The modification mechanism mainly includes the following aspects:
Enhanced thermal conductivity: The addition of bronze powder increases the thermal conductivity of PTFE from 0.25 W/(m·K) to 0.5 W/(m·K), effectively improving heat dissipation performance and thermal stress distribution under high-temperature working conditions.
Improved dimensional stability: The compression set rate of the filled material decreases from 25% to below 5%, maintaining good geometric accuracy within the temperature range of -45℃ to 200℃.
Enhanced extrusion resistance: The formed bronze powder network structure strengthens the material's extrusion resistance. Under a high pressure of 60 MPa, the extrusion resistance strength can reach 35 MPa, which is 175% of that of pure PTFE.

II. Material Selection for Elastomer O-Rings
The O-rings matched with Steck seals usually use NBR or FKM rubber, and differentiated selection is made according to medium characteristics:
NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) is suitable for mineral oil-based hydraulic oils. The acrylonitrile content ranging from 18% to 50% can balance oil resistance and low-temperature performance (with a minimum service temperature of -40℃). Its polar cyano group (–CN) has good affinity for petroleum-based media, but it is not suitable for ester oils and strong oxidant environments.
FKM (fluororubber) is copolymerized from vinylidene fluoride (VDF) and hexafluoropropylene (HFP), with a fluorine content of 66%–70%. It can withstand synthetic ester oils and high temperatures above 150℃. The C–F bond energy is as high as 485 kJ/mol, providing excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, fuel oils and other media.
III. Material Synergistic Working Mechanism
The excellent sealing performance of Steck seals stems from the dynamic synergistic system composed of PTFE step rings and elastomer O-rings.
Dynamic compensation is the foundation. The O-ring provides continuous elastic force with a pre-compression amount of 15%-25%, which can automatically compensate for the wear gap of the PTFE ring during operation and ensure long-term stable sealing.
Interface bonding is the bridge. The surface of PTFE is activated with a sodium-naphthalene complex, reducing its contact angle from 115° to 70° significantly. This enables firm bonding with rubber up to 5 MPa, ensuring the integrity of the assembly under dynamic working conditions.
Pressure response is the key. Under high pressure, when the PTFE ring undergoes cold flow deformation, the O-ring behind it can provide adaptive support through a maximum volume compression of 30%, converting the system pressure into continuous sealing contact pressure to jointly resist medium extrusion.
These three mechanisms work closely together, forming a reliable sealing core for Steck seals to cope with complex working conditions.

IV. Material Adaptation in Engineering Applications
For different working conditions, Mascot recommends the following material combination solutions:
Metallurgical equipment: The combination of FKM O-rings and PTFE rings filled with 25% glass fiber is adopted, which can withstand the radiant heat of 800℃ and acid mist corrosion environment of continuous casting machines.
Polar machinery: NBR with high acrylonitrile content (40%) is matched with bronze powder-filled PTFE, which can still maintain good elasticity and sealing performance at an extremely low temperature of -60℃.
Mining machinery: The combination of FKM and molybdenum disulfide-modified PTFE is used, with an additional dust-scraping auxiliary lip structure. Its service life can be increased by 50% compared with the standard configuration.


